
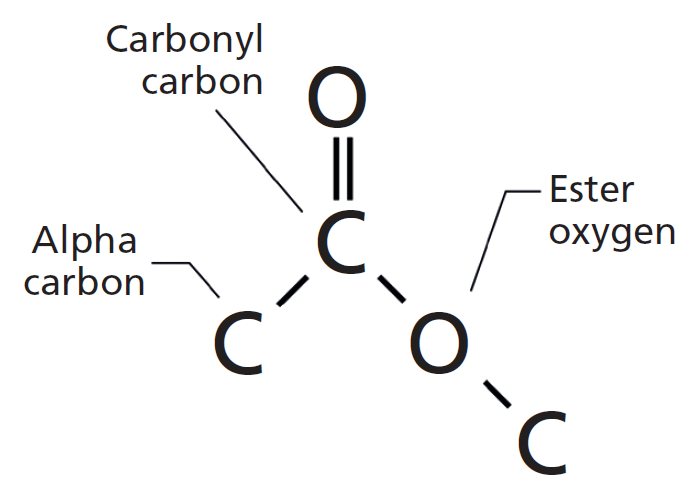
Also as with aldehydes, the C atom in the functional group is counted as one of the C atoms that defines the parent hydrocarbon name. As with aldehydes, the functional group in carboxylic acids is at the end of a carbon chain. Molecules with a carboxyl group are called carboxylic acids. The combination of a carbonyl functional group and a hydroxyl group makes the carboxyl group. Its structure is:ĭraw the structure of methyl butyl ketone. This molecule has five C atoms in a chain, with the carbonyl group on the second C atom. So propanone can also be called dimethyl ketone, while butan-2-one is called methyl ethyl ketone. There is a non-IUPAC way to name ketones that is commonly used as well: name the alkyl groups that are attached to the carbonyl group and add the word ketone to the name. With larger ketones, we must use a locant number to indicate the position of the carbonyl group just before the suffix, as we did with alkenes and alkynes: The common name for propanone is acetone. When naming a ketone, we take the name of the parent hydrocarbon and change the suffix to – one:

The smallest ketone has three C atoms in it. Despite the fact that aldehydes and ketones have the same carbonyl group, they have different chemical and physical properties and are properly grouped as two different types of compounds. This type of molecule is called a ketone. The main thing to note about aldehydes is that the carbonyl group is at the end of a carbon chain.Ī carbonyl group in the middle of a carbon chain implies that both remaining bonds of the carbonyl group are made to C atoms. Methanal has a common name with which you may be familiar: formaldehyde. (Do not confuse – al with – ol, which is the suffix used for alcohols.) So we have: The parent name of the hydrocarbon is used, but the suffix – al is appended. When naming aldehydes, the main chain of C atoms must include the carbon in the carbonyl group, which is numbered as position 1 in the carbon chain. If one bond of the carbonyl group is made to a hydrogen atom, then the molecule is further classified as an aldehyde. In this diagram, the R group represents any hydrocarbon chain: A carbonyl group is formed when an O atom and a C atom are joined by a double bond. There are other functional groups that contain oxygen atoms. Use proper naming conventions for aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, and ester- and ether-containing molecules.Identify the aldehyde, ketone, acid, ester, and ether functional groups.Smaller ether molecules that are liquids at room temperature are common solvents for organic chemical reactions. Diethyl ether, another ether, was once used as an anesthetic, but its flammability and toxicity caused it to fall out of favor. In this case, the R groups are named sequentially, and the word ether is appended. Naming ethers is like the alternate way of naming ketones. The two R groups may be the same or different. functional group is an O atom that is bonded to two organic groups: R-O-R′ anion:įinally, the ether A functional group that has an O atom attached to two organic groups. The H atom in the carboxyl group comes off as the H + ion, leaving a carboxylate A negatively charged ion derived from a carboxylic acid. But no carboxylic acid approaches the 100% dissociation amount required by the definition of a strong acid.Īs their name suggests, however, carboxylic acids do act like acids in the presence of bases. Some carboxylic acids are stronger-for example, trichloroacetic acid is about 45% dissociated in aqueous solution. A 1 M solution of formic acid is only about 1.3% dissociated into H + ions and formate ions, while a similar solution of acetic acid is ionized by about only 0.4%. (For more information about strong acids, see Chapter 12 "Acids and Bases", Section 12.4 "Strong and Weak Acids and Bases and Their Salts".) This means that all carboxylic acids are weak acids. No carboxylic acid is on the list of strong acids ( Table 12.2 "Strong Acids and Bases"). How acidic are carboxylic acids? It turns out that they are not very acidic. Formic acid is the compound that makes certain ant bites sting, while acetic acid is the active substance in vinegar. Methanoic acid and ethanoic acid are also called formic acid and acetic acid, respectively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
